How to Choose the Perfect Generator for Your Home Power Needs
Introduction
When the lights go out, having a reliable generator can make all the difference. Whether you’re preparing for unexpected power outages or looking to keep essential appliances running during storms, choosing the right generator for your home is key. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to find the perfect generator that fits your household’s power needs, budget, and lifestyle.
When selecting a generator for residential use, it’s essential to understand the differences between standby and portable generators to determine which best suits your needs.
Standby Generators

Standby generators are permanently installed and connected to your home’s electrical system. They automatically detect power outages and start within seconds, providing seamless backup power. These generators can supply sufficient power to run an entire home, including heating and cooling systems, appliances, and electronics. Typically powered by natural gas or propane, standby generators have a continuous fuel source, eliminating the need for manual refuelling.
Considerations: Standby generators involve higher upfront costs and require professional installation, which can add to the overall expense. Regular maintenance by certified professionals is necessary to ensure reliable operation.
Portable Generators

Portable generators are generally less expensive than standby units, making them accessible for many homeowners. These generators can be moved to different locations as needed, providing flexibility for various uses, including outdoor activities. Portable generators do not require professional installation; they can be set up and operated manually.
Considerations: They require manual startup and connection during power outages, which may not be ideal during emergencies. Portable generators typically have lower power outputs, suitable for running essential appliances but not an entire home. They often run on gasoline or diesel, necessitating safe fuel storage and manual refuelling during extended use.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Home
Consider the following factors to determine the best generator for your residential needs:
Power Requirements: Assess the essential appliances and systems you need to power during an outage. Standby generators are suitable for whole-home backup, while portable generators can handle critical devices.
Budget: Evaluate your budget, keeping in mind that standby generators have higher upfront and installation costs, whereas portable generators are more budget-friendly.
Frequency of Power Outages: If you experience frequent or prolonged outages, a standby generator offers reliable, automatic power. For occasional outages, a portable generator may suffice.
Installation and Maintenance: Consider whether you prefer a system that requires professional installation and regular maintenance (standby) or a more hands-on approach with manual setup and upkeep (portable).
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a generator that ensures your home remains powered during outages, aligning with your specific needs and circumstances.
Difference between portable generators Vs standby generators?
Here’s a detailed comparison between portable generators and standby generators to help understand their key differences

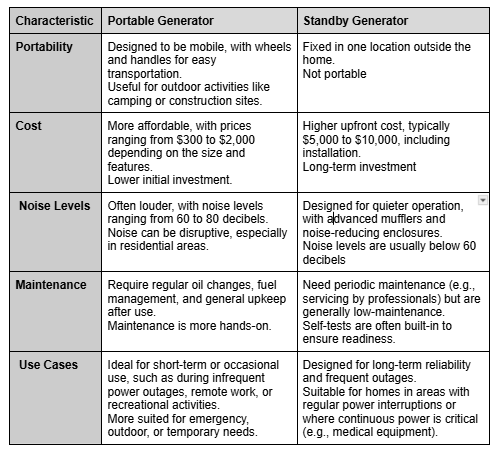
Important factors to consider when selecting a suitable generator
Selecting the right generator involves evaluating several important factors to ensure it meets your power needs, budget, and circumstances.
Here are the key factors to consider:
Power Requirements:
List the essential appliances and systems you want to power (e.g., refrigerator, lights, HVAC, medical equipment). Calculate the total wattage of these devices. Remember to include both starting watts (for appliances with motors) and running watts. Choose a generator that can handle your total power requirements with some extra capacity for safety.
Type of Generator
Portable Generators: Ideal for short-term, occasional use, and outdoor activities. Typically lower cost but require manual operation.
Standby Generators: Best for long-term, seamless home backup power. Higher cost but automatic operation and greater reliability.
Inverter Generators: Provide clean power for sensitive electronics (e.g., laptops, phones). Quieter and more fuel-efficient than traditional portable generators.
Fuel Type
Gasoline: Readily available but requires frequent refuelling and has a shorter shelf life.
Propane: Cleaner burning with longer shelf life; often used for standby generators.
Natural Gas: Continuous supply from your home’s gas line; convenient for standby units.
Diesel: Offers higher efficiency and longer runtime but may not be as widely available.
Dual-Fuel or Tri-Fuel Options: Flexible generators that can run on more than one fuel type.
Runtime and Fuel Efficiency
Check how long the generator can run on a full tank or continuous fuel supply. For extended outages, look for generators with larger fuel tanks or standby models connected to an uninterrupted fuel source (like natural gas).
Portability
If you need to move the generator (e.g., for camping or work sites), look for lightweight models with wheels and handles. Standby generators are permanently installed and not portable.
Noise Level:
Generators can be noisy, which may be a concern for residential areas or camping.
Portable Generators: Typically louder (60–80 dB).
Inverter and Standby Generators: Quieter, often under 60 dB, with noise-reducing technology.
Budget;
Portable Generators: £235 – £1560
Inverter Generators: £390 – £2340
Standby Generators: £3900 – £7800+ (including installation).
Factor in long-term costs, including fuel, maintenance, and potential installation expenses.
Safety Features:
Look for built-in safety mechanisms:
Low-Oil Shutdown: Automatically turns off the generator to prevent engine damage.
Surge Protection: Prevents damage to connected devices from power surges.
CO Sensors: Detects dangerous levels of carbon monoxide and shuts down the generator.
Always operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas to avoid CO poisoning.
Ease of Use
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Automatically switches power to a standby generator during an outage.
Electric Start: Simplifies starting; avoids manual pull cords.
Control Panel: Easy-to-read interface with indicators for fuel level, runtime, and maintenance alerts.
Maintenance and Support:
Regular maintenance is crucial for generator longevity. Consider the availability of replacement parts, service centers, and warranties.
Weather and Location Suitability:
Choose a weather-resistant generator if you live in an area prone to harsh weather conditions. Ensure it’s rated for outdoor use and can withstand your local climate.
Compliance with Local Regulations:
Check local codes for noise limits, emissions standards, and installation requirements. Look for CARB or EPA-compliant generators for environmentally-friendly options.
Brand and Reviews:
Opt for reputable brands with a history of reliability and positive customer reviews.
Additional Features
Remote Monitoring: Allows you to monitor and control your generator from a smartphone.
Parallel Capability: Enables you to connect two generators for increased power.
USB Ports and Extra Outlets: Useful for charging small devices directly.
Summary Table: Key Considerations

By balancing these factors, you can select a generator that meets your specific needs, whether for emergencies, outdoor use, or long-term home backup.
Interested in our Electrical Engineering Courses?
At iLearn Engineering®, we offer a diverse range of online accredited electrical engineering courses and qualifications to cater to different academic and career goals. Our courses are available in varying credit values and levels, ranging from 40 credit Engineering Diplomas to a 360 credit International Graduate Diploma.
Short Courses (40 Credits)
A selection of our more popular 40 credit electrical diplomas…
Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Diploma in Electrical Technology
Diploma in Renewable Energy (Electrical)
First Year of Undergraduate (Level 4 – 120 Credits)
Higher International Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
First Two Years of Undergraduate (Level 5 – 240 Credits)
Higher International Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering.
Degree equivalent Graduate Diploma (Level 6 – 360 Credits)
International Graduate Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
All Electrical and Electronic Courses
You can read more about our selection of accredited online Electrical and Electronic Engineering courses here.
Complete Engineering Course Catalogue (all courses)
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

