Determine the deflection of en-castre beams.
Following on from our previous article on deflection of beams with a combined load, we’re going to look at deflection in a different type of beam.
What is an en-castre beam?
En-castre beams, or fixed beams, have fixed supports at both ends. So, they don’t allow horizontal, vertical or rotational movement of that support.
The most important characteristic of this beam is that the slope and deflection are zero at both ends.
The below image shows an en-castre beam:

Encastre beams can also be built in walls, as you can see in the image below:

Advantages and Disadvantages of Encastre Beams
En-castre beams have some benefits, including:
- For the same span and load, fixed beams have lower bending moments than simply supported beams.
- Due to their support fixity, smaller deflections are encountered in fixed beams than in simply supported beams.
However, encastre beams also have some disadvantages. In encastre beams, if the condition of fixity at the ends is disturbed, for example, by settlement and rotational yield of supports, the consequence is that large bending moments will be induced in the beam to counter this effect. Moreover, in the case where there are changes in temperature, this will create large stresses in the section.
Structural Action of a Fixed Beam
When a fixed beam is subjected to loads, it bends, developing resisting moments and shears. The deflected shape of the beam is shown in this image:

Note that the slope and deflection at the ends A and B are zero, as they are restrained. The beam ‘sags’ for a part of its length in the middle and ‘hogs’ at the ends. This necessarily produces two points of inflection (contraflexure) corresponding to the change in the bending moment (BM).
Calculating Deflection of En-castre Beams
A standard data table can be used for the determination of deflection, moments and shear force in a fixed beam:
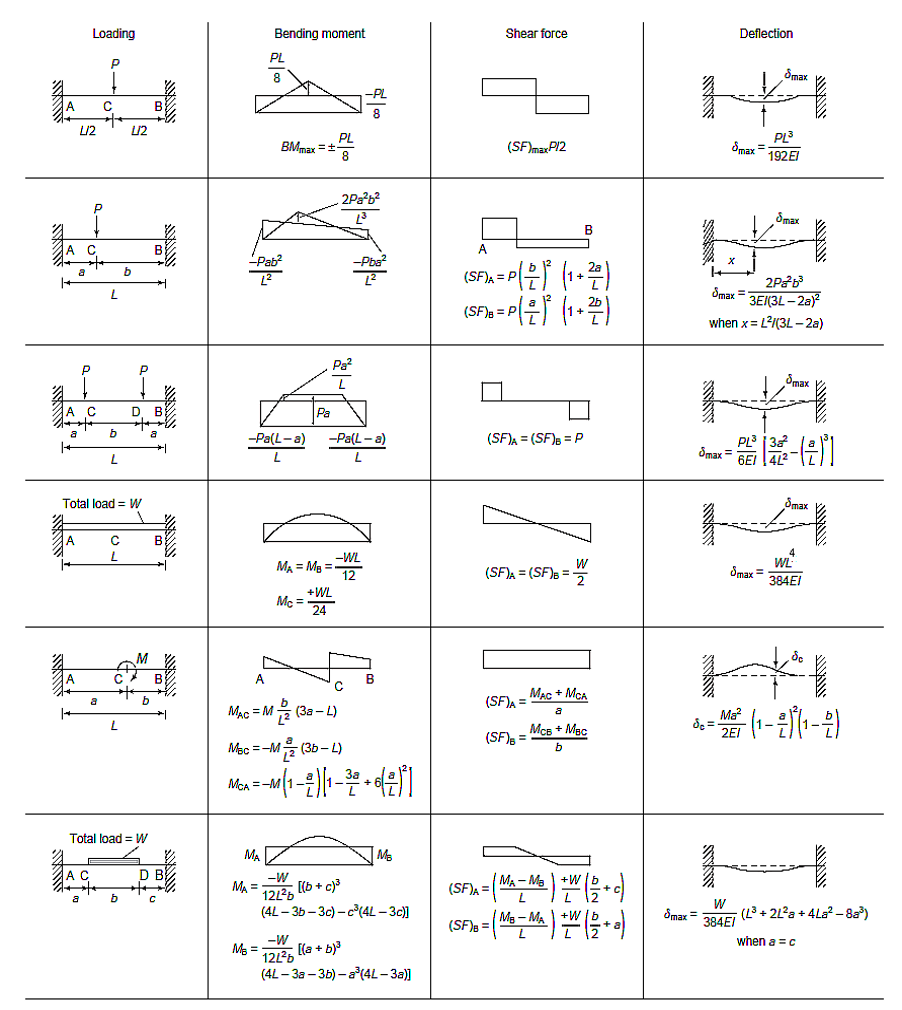
Let’s check out an example and see how we would go about calculating the deflection. A fixed beam of 6m span is loaded with point loads of 150 kN at 2m from each support. We’re going to find the maximum deflection.
Take E = 2 x 108 kN/m2 and I = 8 x 108 mm4

Load = 150 kN = 150000 N
Length of beam = 6m
I = 8 × 108 mm4 = 0.0008 m4
E = 2 × 108 kN/m2
For this loading arrangement case, the table gives the maximum deflection as
max = Pl36EI3a24l2-(al)3
Hence, substituting the values gives
= 1500006362 × 10110.0008322462-(26)3
= 0.03375(0.0833 – 0.037037)
max= 0.00156 m
Keep an eye out for future articles on more deflection calculations.
Interested in our courses?
Interested in civil or mechanical engineering? Find out more about all the civil engineering courses we have available by clicking here, and the mechanical engineering courses by clicking here.
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Technology
Diploma in Sustainable Construction
Diploma in Structural Engineering
Diploma in Building and Construction Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Civil Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Civil Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Mechanical Engineering
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

