How can we select engineering materials?
In our previous article, we looked at elastic and magnetic hysteresis. In this article, we’re going to look at how we can select engineering materials. In other articles, we have previously looked at the different materials and their properties. However, it’s important that engineers understand how we can go about picking the correct material for our engineering application.
Material selection charts
These charts are a graphical way of representing material data. As the majority of mechanical properties range of several orders of magnitude, the charts are produced with a logarithmic scale.
The image below shows an example chart for Young’s modulus versus density for certain material families, such as ceramics, wood, metals and so on:
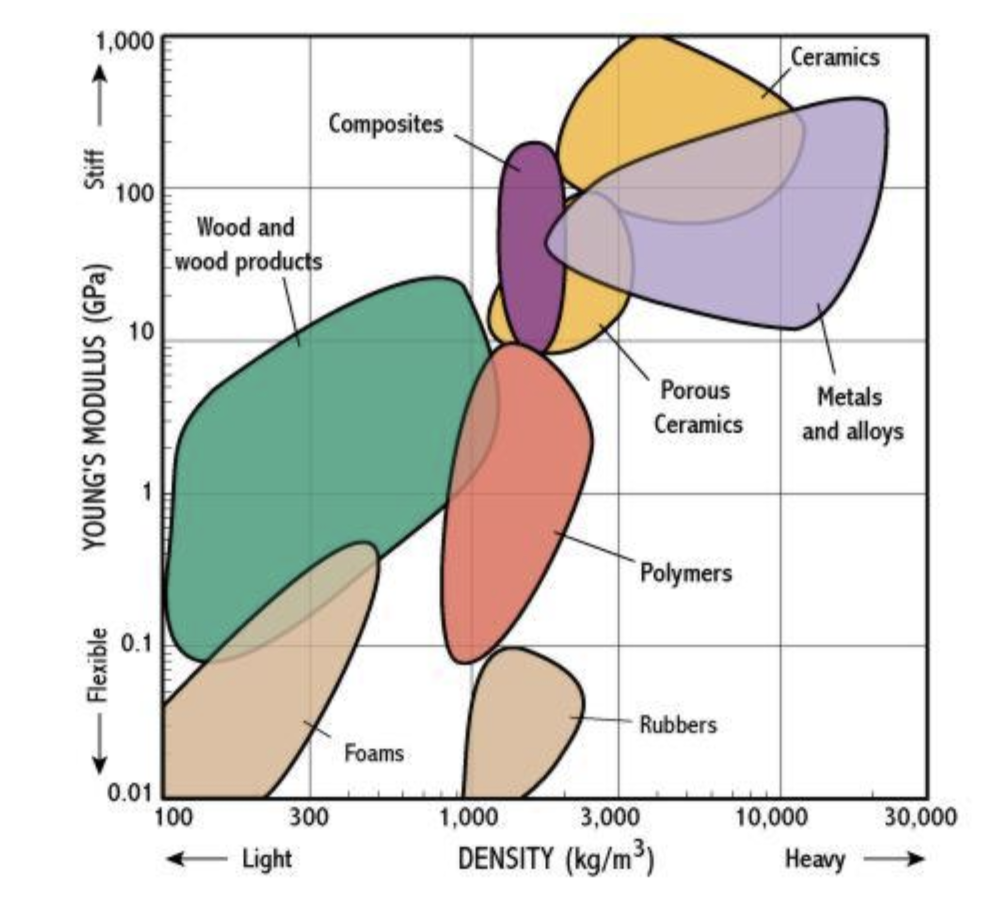
On the Y-axis, you can see that the values for Young’s modulus are given in GPa. With a logarithmic scale being used, a wide range of values from 0.01GPa (10MPa), i.e. very flexible materials, all the way through to 1000GPa (very stiff materials) can easily be shown.
On the x-axis we have material density, going from light materials through to heavy materials. Each coloured ‘bubble’ represents a whole material family, so we can quickly see how different materials types measure. For example, it is no surprise to see that wood and wood products are generally lower density (and therefore weight) than metals and alloys.
Each ‘bubble’ can then be further split down to show the individual material properties within that classification. For example, the Young’s modulus vs density chart is now shown with metals and polymers expanded into more detail:
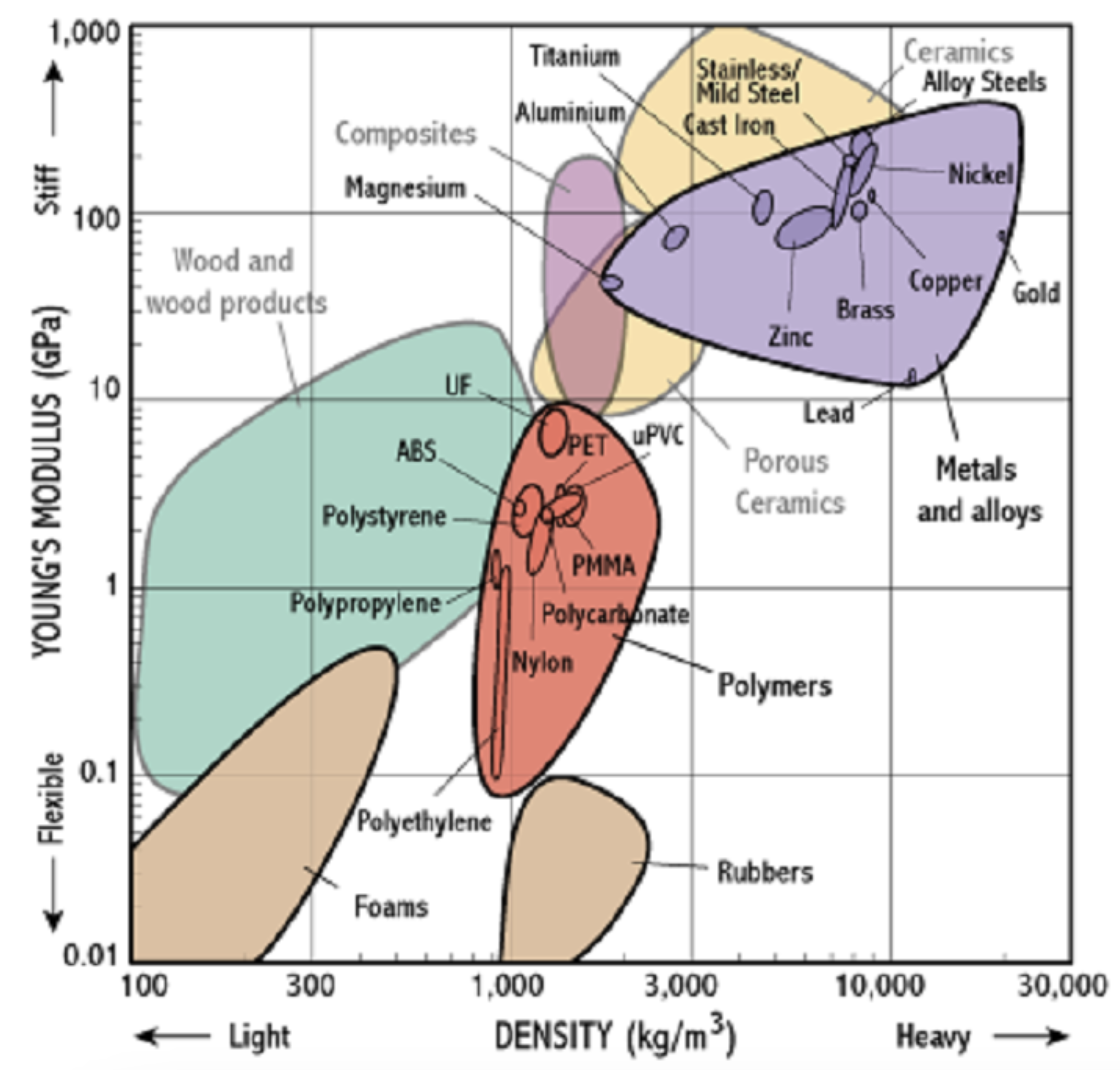
It’s worth noting how each specific material takes up a much smaller ‘bubble’, so now the chart starts to become much more useful for material selection purposes, and engineers can dive a lot deeper into selecting a specific material, for example copper rather than a generic ‘metal’.
Engineering designers have a challenging task in choosing the appropriate material for any given product. It is common for them to have to consider many competing objectives and constraints at once – light and stiff, strong and cheap, tough and recyclable (or maybe all of these at once!). Material selection in design is therefore a matter of assessing trade-offs between several competing requirements, and the material selection charts help to visualise these trade-offs, making it a lot easier for engineering designers to visualise how various materials might affect their design. This makes it a lot easier to select an appropriate material overall.
Keep an eye out for our next articles looking at basic electrical parameters and how we calculate them.
Interested in our courses?
You can read more about our selection of accredited online mechanical and industrial engineering courses here.
Check out individual courses pages below:
Higher International Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Technology
Higher International Diploma in Industrial Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Industrial Engineering
Diploma in Engineering Management
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

