What is a PLC system?
In our previous articles, we discussed various aspects of digital electronics, including the application of Thevenin’s theorem. Now we’re going to look at PLC systems, what they are and why they might be used.
What is a PLC?
PLC stands for “programmable logic controller”. They are used to automate industrial processes as they can operate in extreme environments. These environments can include extreme temperatures, dusty conditions, or wet conditions. A PLC can perform discrete and continuous functions needed in industry. They can also be programmed and reprogrammed whenever needed via control systems.
The main advantage of a PLC over a “hard-wired” control system is that they can be reprogrammed with very little cost or time. In a hard-wired control system, we would have to rip out wires and start from scratch. It is a lot more expensive and takes a lot longer.
For example, when you switch on a light, it operates under two conditions: ON and OFF. If you want a delay before the light operates, you can use one of two methods:
Hard-wired setup: the only way to achieve this is to completely rewire our circuit to add a timing relay.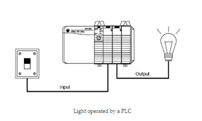
PLC: change to the code in the programme, no additional wiring and hardware to make sure of a change.
How does a PLC work?
A PLC can be understood as a cyclic scanning method known as the scan cycle. A PLC scan process includes these steps: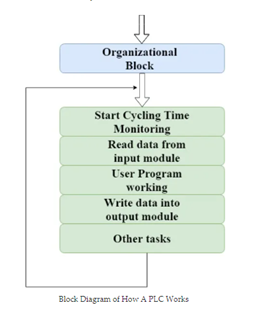
- The operating system starts cycling and monitoring of time.
- The CPU starts reading the data from the input module and checks the status of all the inputs.
- The CPU starts executing the user or application program written in relay-ladder logic or any other PLC-programming language.
- The CPU performs all the internal diagnosis and communication tasks.
According to the program results, it writes the data into the output module so that all outputs are updated. This process continues as long as the PLC is in run mode.
Types of PLCs
There are two main types of PLC:
- Compact PLC: many modules combined in a single case, fixed number of I/O modules and external I/O cards. Modules can be added but does not have the capability to expand the modules. Every input and output would be decided by the manufacturer.
- Modular PLC: this type of PLC permits multiple expansion through “modules”, hence referred to as Modular PLC. I/O components can be increased. It is easier to use because each component is independent of the other.

PLCs are divided into three types based on output: namely Relay output, Transistor output, and Triac Output PLC. The relay output type is best suited for both AC and DC output devices. Transistor output type PLC uses switching operations and is used inside microprocessors.
Applications of the PLC
PLC’s have a variety of applications and uses, such as the glass and paper industries, cement manufacturing, and in process automation plants.
The advantages of PLC´s include:
- very faster scan time.
- capable of communication with computers in the plant.
- great computational capabilities.
- shorter training time is required.
- A wide range of control applications.
- easily programmed and has an easily understood programming language.
- the project cost can be accurately calculated.
- supervisory control capability.
- small physical size.
- flexibility in programming and reprogramming.
- Troubleshooting is easier and faster.
- high-speed counters.
- shorter project implementation time.
- reliability in operation.
The disadvantages of PLCs include:
- When a problem occurs, hold-up time is indefinite and usually long
- There are limitations to the working of PLCs under high temperatures and vibration conditions.
- Some PLCs turn on when power is restored and may cause an accident.
Keep an eye out for our next articles, where we’re going to dive even further into Programmable Logic Controller systems and their uses.
Interested in our courses?
You can read more about our selection of accredited online electrical and electronic engineering courses here.
Check out individual courses pages below:
Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Diploma in Electrical Technology
Diploma in Renewable Energy (Electrical)
Higher International Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

