How to Calculate Inertia for Standard Shapes
Inertia, specifically rotational inertia or moment of inertia, not only depends on how much mass an object has, but also on how that mass is distributed relative to the axis of rotation.
Different shapes have different geometries, which causes their mass to be positioned at varying distances from the axis. The farther the mass is from the axis, the greater the resistance to rotational motion.
For example:
-
A solid cylinder has more mass concentrated near the axis → lower moment of inertia.
-
A hollow cylinder has mass farther from the axis → higher moment of inertia.
-
A thin rod rotating about its centre has less resistance than the same rod rotating about one end.
This is why each shape has its own unique formula for moment of inertia—reflecting both its mass and geometry.
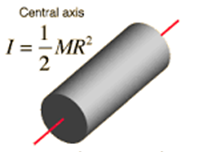
Solid Cylinder
A solid cylinder is a common shape in engineering, found in components like rollers, shafts, and flywheels. When it rotates about its central (longitudinal) axis, its moment of inertia is given by:
I = ½ MR2
Example
A solid cylinder has:
- Mass M = 8 kg
- Radius R = 0.3 m
I = ½ MR2
I = ½ × 8 × (0.3)2
I = 0.5 × 8 × 0.09 = 0.36 kg⋅m2
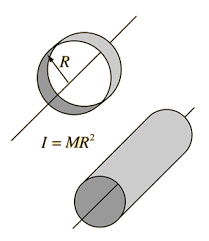
Hollow Cylinder
A hollow cylinder (also called a cylindrical shell) is a tube-like structure where all the mass is concentrated at a fixed distance from the central axis. When it rotates about this central (longitudinal) axis, the moment of inertia is
I = MR2
Example
A hollow cylindrical shell (thin-walled) has:
- Mass M = 6 kg
- Radius R = 0.5 m
For a thin-walled hollow cylinder, all the mass is assumed to be at a fixed distance R from the axis. The moment of inertia is given by:
I = MR2
I = 6 × (0.5)2
I = 6 × 0.25 = 1.5 kg⋅m2
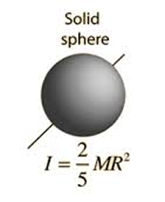
Solid Sphere
A solid sphere is a perfectly round object with mass distributed uniformly throughout its volume. When it rotates about an axis through its centre (like a spinning ball), its moment of inertia is
I = ⅖ MR2
Example
A solid sphere has:
- Mass M = 4 kg
- Radius R = 0.2 m
For a solid sphere rotating about its center (through its diameter), the moment of inertia is:
I = ⅖ MR2
I = ⅖ × 4 × (0.2)2
I = ⅖ × 4 × 0.04
I = 0.064kg⋅m2
Thin Rod, with axis at the centre
A thin, uniform rod has mass distributed evenly along its length. When it rotates about an axis perpendicular to its length and passing through its centre (like a baton spinning in the air), the moment of inertia is
I = 1/12 ML2
Example
A thin, uniform rod has:
- Mass M = 2 kg
- Length L = 1.5 m
When the rotation axis is at the center of the rod and perpendicular to its length, the moment of inertia is:
I = 1/12 ML2
I = 1/12 × 2 × (1.5)2
I = 1/12 × 2 × 2.25
I = 0.375kg⋅m2
Thin Rod with axis at the end
A thin, uniform rod with rotation about an axis perpendicular to its length and passing through one end (like a door swinging on a hinge) has a moment of inertia given by:
I = ⅓ ML2
Example
A thin rod of length 2 m and mass 3 kg is rotating about one of its ends perpendicular to its length. What is the moment of inertia?
I = ⅓ ML2
Where:
- M 3 kg
- L = 2 m
I = ⅓ × 3 × (2)2
I = 1×4 = 4 kg⋅m2
So, the moment of inertia is 4 kg·m².
The larger the moment of inertia, the harder it is to rotate the object.
Units of moment of inertia: kg⋅m2
Interested in our engineering courses?
We have over 70 courses across all major engineering disciplines, including, mechanical, electrical and electronic, civil, aerospace, industrial, computer and general engineering. Visit our course catalogue for a complete list of fully accredited engineering programmes.
A small selection of short courses …
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Structural Engineering
Level 6 Courses
International Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
International Graduate Diploma in Civil Engineering
International Graduate Diploma in Aerospace Engineering
Level 5 Courses
Higher International Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Civil Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Aerospace Engineering
Level 4 Courses
Higher International Certificate in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Civil Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Aerospace Engineering
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

